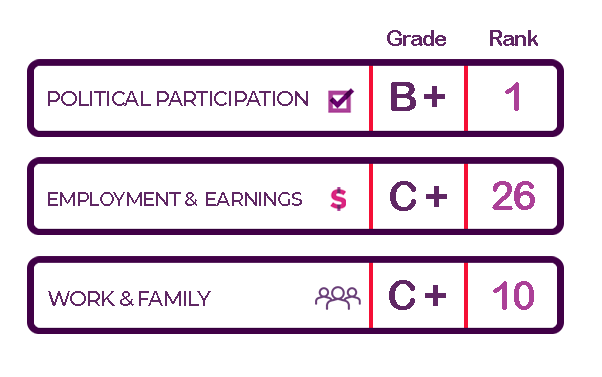
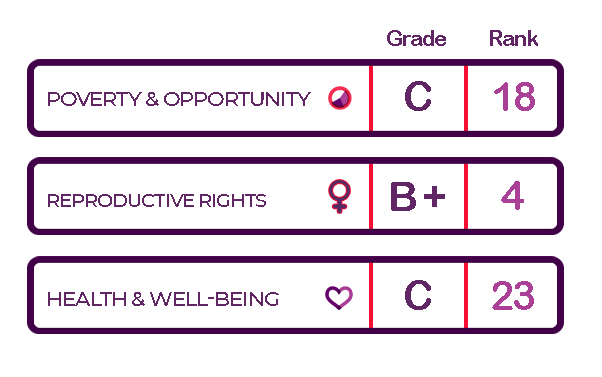
The Status of Women in the States project ranks and grades Maine across several areas of women’s lives. While Maine performs better in some areas, no matter the rank, there are still barriers and inequities that prevent women from succeeding and thriving. Across all indices, Maine ranks toward the top of states in the country. Maines’s performance is the strongest on the Political Participation and Reproductive Rights indices. Maines’s performance is weakest on the Employment and Earnings and the Health and Well-Being indices.
Explore the Data
As state policies and programs have changed over the years, so has the status of women in Maine. Since 1996, Maine has made progress in some areas, while lagging in others.
Articles and Publications
Gender and Racial Wage Gaps Persist as the Economy Recovers
Download Fact Sheet Download Quick Figure As a sign of the uneven recovery in 2021, gender wage gaps narrowed while median earnings fell marginally. Research Highlights As the economy slowly recovered from the COVID-19 “She-cession” and women and men began [...]
Fixing the Child Care Staffing Shortage by Making Child Care Jobs “Good Jobs”
Download Report Child care is an essential support for parents’ full participation in the economy, education, and training, and for children’s growth and development into healthy and well-adjusted adults. Even before the COVID-19 pandemic’s onset, however, high-quality and affordable child care was [...]
IWPR Reproductive Rights Index: A State-by-State Analysis and Ranking
Download Report The Status of Women in the States Initiative at the Institute for Women’s Policy Research provides timely data and research on women’s progress and well-being in the United States on a number of important indicators: employment and earnings, political participation, [...]




